Bile duct cancer starts in the bile ducts, which are thin tubes between the liver and the small intestine. The ducts move bile (a greenish-brown alkaline fluid that aids digestion) from the liver and gallbladder to the small intestine, where it helps digest the fats in food.
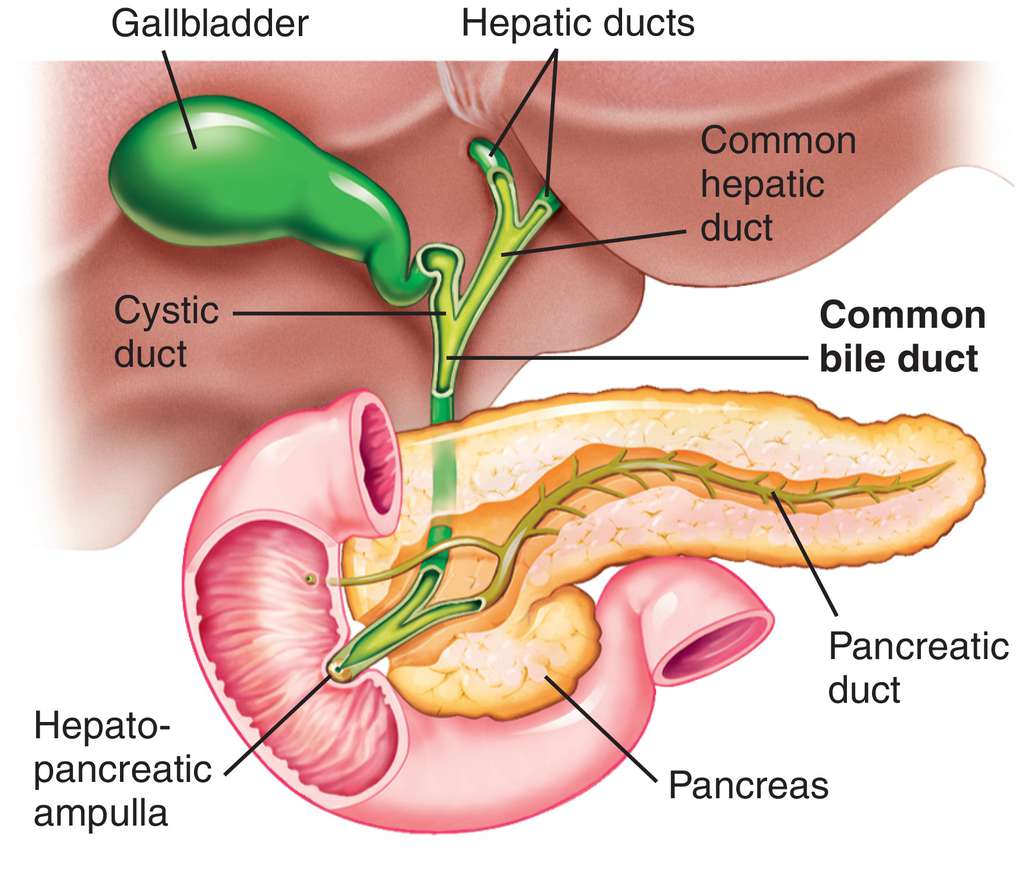
Depending on where it's located in the bile duct system, cancer is classified into three types:
• Intrahepatic bile duct cancers
• Perihilar (also known as hilar) bile duct cancers
• Distal bile duct cancers


Nearly all bile duct cancers are called cholangiocarcinomas (composed of mutated epithelial cells). Most of these are adenocarcinomas, which are cancers that start in glandular cells. Bile duct adenocarcinomas develop from the mucous gland cells that line the inside of the duct.
Bile duct cancer can affect your body in many ways. As part of the digestive system, bile ducts help digest food properly. If cancer spreads to the liver, the chemical balance of the body will be disturbed.
 Causes & Symptoms
Causes & Symptoms
of Bile Duct Cancer
Researchers do not know the exact cause of most bile duct cancers. However, there seems to be a link between these cancers and things that irritate and inflame the bile ducts — bile duct stones, choledochal cysts, parasites, cirrhosis of the liver, or something else.Bile duct cancer does not usually cause signs or symptoms until later in the course of the disease, but sometimes symptoms can appear sooner and lead to an early diagnosis. Bile duct cancer symptoms include:
• Jaundice
• Itching
• Light-colored / greasy stools
• Dark urine
• Abdominal pain
• Loss of appetite / weight loss
• Fever
• Nausea and vomiting
 Who Gets Bile
Who Gets Bile
Duct Cancer
The average age of people diagnosed with cancer of the intrahepatic bile ducts (within or originating in the liver) is 70, and for cancer of the extrahepatic bile ducts (situated or originating outside the liver), it is 72.Bile duct cancer is more common in men (13 cases per 100,000 people) than women (4.4), and among Asian / Pacific Islander (20.8 for men), Hispanic (19.5) and American Indian / Alaska Native (18.5) populations.
 Prognosis if You
Prognosis if You
Have Bile Duct Cancer
For treatment purposes, doctors often use a simpler system based on whether or not cancer can likely be removed (resected) with surgery:• Resectable cancers are those that doctors believe can be removed completely by surgery.
• Unresectable cancers have spread too far or are in too difficult a place to be removed entirely by surgery.
Generally speaking, most Stage 0, I, and II cancers and possibly some Stage III cancers are resectable. Most Stage III and IV tumors are unresectable.
However, this also depends on other factors, such as the size and location of cancer and whether a person is healthy enough for surgery.
The 5-year relative survival rate for intrahepatic bile duct cancer:
• Stage I – 15 percent
• Stage II and III – 6 percent
• Stage IV – 2 percent
The 5-year relative survival rate for extrahepatic bile duct cancer:
• Stage I – 30 percent
• Stage II and III – 24 percent
• Stage IV – 2 percent
What is naturopathic medicine?
Naturopathic medicine is an approach to health care that uses natural, non-toxic therapies to treat the whole person and encourage the self-healing process. Naturopathic clinicians treat a variety of conditions, including digestive issues, sleep disturbances and chronic fatigue syndrome.As part of the supportive therapy services we offer, our naturopathic oncology providers may suggest therapies to help support normal metabolism and digestion during cancer treatment and help manage side effects, such as nausea or fatigue.
As part of the intake process, you may choose to meet with a naturopathic oncology provider, who will review your history and make suggestions from a wide variety of natural therapies. Your naturopathic oncology provider also will review current supplements to identify potential herb-drug-nutrient interactions.
Other natural therapies our naturopathic medicine team may suggest include:
- Herbal and botanical preparations, such as herbal extracts and teas
- Dietary supplements, such as vitamins, minerals and amino acids
- Homeopathic remedies, such as extremely low doses of plant extracts and minerals
- Physical therapy and exercise therapy, including massage and other gentle techniques used on deep muscles and joints for therapeutic purposes
- Hydrotherapy, which prescribes water-based approaches like hot and cold wraps, and other therapies
- Lifestyle counseling, such as exercise, sleep strategies, stress reduction techniques, as well as foods and nutritional supplements
- Acupuncture, to help with side effects like nausea and vomiting, dry mouth, hot flashes and insomnia
- Chiropractic care, which may include hands-on adjustment, massage, stretching, electronic muscle stimulation, traction, heat, ice and other techniques
No comments:
Post a Comment