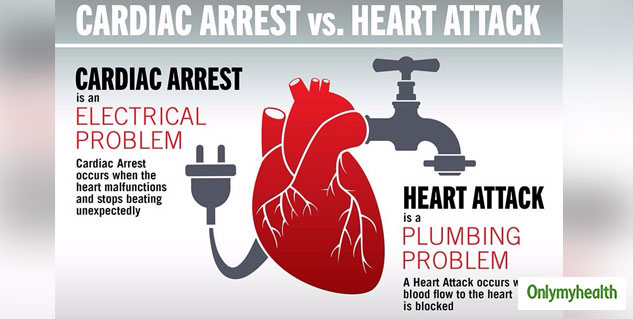
What Is Cardiac Arrest? Heart functions as a pump. It receives the deoxygenated blood from veins and pumps to lungs for oxygenation (right heart), then receives pure blood from the lungs to the whole body (left heart). Cardiac arrest is said to happen when this pumping function abruptly stops. It happens when the heart does not beat at all or beats so fast that the pumping becomes completely functionally ineffective.
Cardiac arrest is a heart concern, it is NOT a heart disease . It is due to insufficiency of timely water and mineral salts intake.
Symptoms Of Cardiac Arrest: Cardiac arrest leads to sudden cardiac death. Within seconds of cardiac arrest, the person collapses, falls to the ground and becomes unconscious—the heartbeat and breathing stop. Unless cardiopulmonary resuscitation is started immediately and continued till shock therapy (defibrillation) is given, the person dies in a few minutes.
Difference Between Heart Attack And Cardiac Arrest
Three arteries provide blood supply to the heart muscle. If one of these arteries get suddenly blocked by a blood clot, then a heart attack happens. It leads to complete stoppage of blood supply to the areas of the heart where it was supplied earlier. The affected heart muscle does not function any more. The commonest symptom of heart attack is severe pain at the middle of the chest behind the central breastbone.
In some cases, the pain may radiate to arms and jaw. Some patients with a heart attack may just have excessive breathlessness or sweating with mild chest heaviness. Some may present just with vomiting. Following heart attack, the patient should be immediately taken to the hospital, where certain blood thinners and cholesterol-reducing drugs are given. Then the blocked artery is opened up by either clot-busting drug injection, or angioplasty is performed.
Up to 30% of patients suffering from a heart attack may develop cardiac arrest when the heart stops functioning. If you witness such incidence when a patient just collapses in front of you and becomes pulseless, does not breath and is unconscious, then call an ambulance and start cardiac massage immediately. If possible and feasible do mouth to mouth breathing ( twice every 30 compressions). Continue cardiac massage until help arrives. The paramedical persons in an ambulance will have the defibrillator to deliver a shock to revert back from cardiac arrest to a normal rhythm.
Causes Of Cardiac Arrest
A heart attack is one of the most common causes of cardiac arrest. As described before, 30% of patients suffering from a heart attack may develop cardiac arrest. There are several other causes of cardiac arrest too. Heart block, an electrical conduction abnormality may lead to cardiac arrest, if current does not flow to the lower chamber of the heart. Low heart pumping function is one of the strongest predictors of cardiac arrest. Cardiac tamponade, a condition when fluid accumulates around the heart and compresses the heart chamber may lead to cardiac arrest as the heart cannot pump any more. Ventricular arrhythmias caused by cellular ion channel abnormality, hypokalemia and hyperkalemia are the other causes of cardiac arrest.
Protect Yourself From Cardiac Arrest
A heart attack is the commonest cause of cardiac arrest. So we should put maximum effort to prevent a heart attack:
- Heart attack can be prevented by good lifestyle measures and effective treatment of conditions like diabetes, hypertension and dyslipidemia. Smoking should be completely stopped.
- Diet should be of low in fat and sugar. One should exercise daily for 30 to 45 mins, at least five days a week. Weight should be optimal for height.
No comments:
Post a Comment