Generating terahertz radiation from water makes 'the impossible, possible'
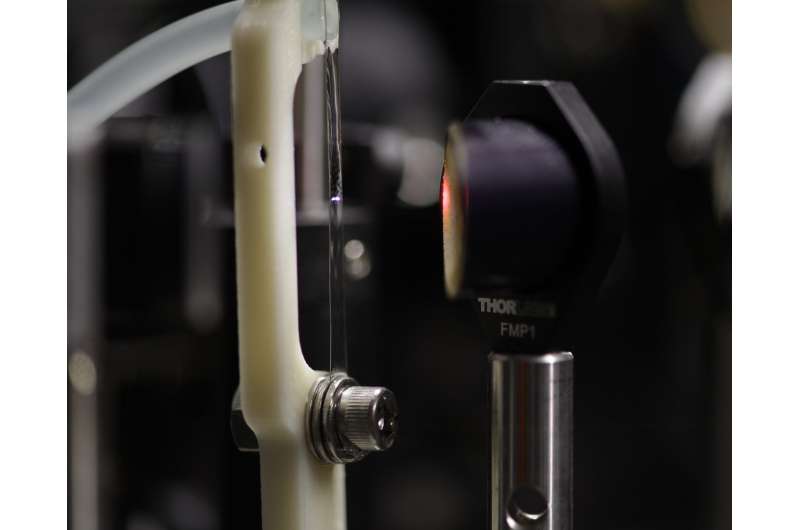
Researchers use lasers to generate terahertz pulses via interaction with a target. In this case, the target was an extremely thin water film -- approximately 200 microns or about the thickness of two pieces of paper -- created using water suspended between two aluminum wires. Credit: University of Rochester photo / Kaia Williams
Xi-Cheng Zhang has worked for nearly a decade to solve a scientific puzzle that many in the research community believed to be impossible: producing terahertz waves—a form of electromagnetic radiation in the far infrared frequency range—from liquid water.
Now, as reported in a paper published in Applied Physics Letters, researchers at the University of Rochester have "made the impossible, possible," says Zhang, the M. Parker Givens Professor of Optics. "Figuring out how to generate terahertz waves from liquid water is a fundamental breakthrough because water is such an important element in the human body and on Earth."
Terahertz waves have attracted increased attention recently because of their ability to nondestructively pass through solid objects, including those made of cloth, paper, wood, plastic, and ceramics, and produce images of the interiors of the objects. Additionally, the energy of a terahertz photon is weaker than an x-ray photon. Unlike x-rays, terahertz waves are non-ionizing—they do not have enough energy to remove an electron from an atom—so they do not have the same harmful effects on human tissue and DNA.
Because of these abilities, terahertz waves have unique applications in imaging and spectroscopy—everything from discovering bombs in suspicious packages, to identifying murals hidden beneath coats of paint, to detecting tooth decay.
"Terahertz waves have a capacity to see through clothing, which is why you have these sub-terahertz body scanners at airports," Zhang says. "These waves can help to identify if an object is explosive, chemical, or biological, even if they can't tell exactly what the object is."
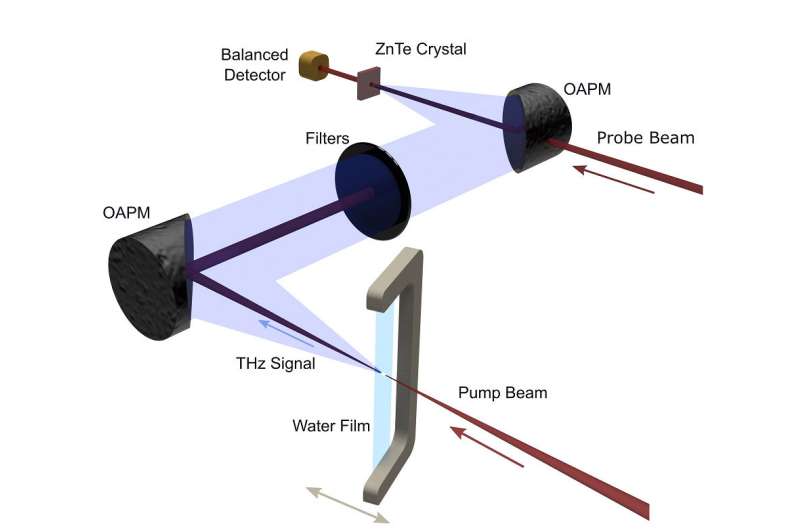
Zhang's research group uses lasers to generate terahertz pulses via interaction with a target. In this case, the target is an extremely thin film of water—approximately 200 microns or about the thickness of two pieces of paper—created using water suspended by surface tension between two aluminum wires. Researchers focus a laser into the water film, which acts as an emitter for the terahertz radiation output.
Previous researchers have generated terahertz waves from targets of solid crystals, metals, air plasma, and water vapor, but, until now, liquid water has proved elusive.
The experimental set-up used to generate terahertz waves from liquid water. Researchers focus the optical pump beam into the water film and use a series of filters and off-axis parabolic mirrors (OAPMs) to detect the terahertz signal and block any other light waves simultaneously generated from the water film. Credit: University of Rochester / Xi-Cheng Zhang Lab
"Water was considered the enemy of terahertz waves because of water's strong absorption," Zhang says. "We always tried to avoid water, but it is a surprisingly efficient terahertz source."
In fact, when researchers measured the terahertz waves generated by the water, they found they were 1.8 times stronger than the terahertz waves generated from air plasma under comparable experimental conditions.
Because water is such a strong absorber, however, many people in the research community believed it would be impossible to use water as a target. Zhang himself has spent years attempting a solution, and he found a likewise stalwart in Qi Jin, now a PhD candidate in optics at Rochester, and the lead author on the paper.
"Almost everybody thought we wouldn't be able to get a signal from water," Jin says. "At first, I didn't believe it either."
One of the challenges was creating a film of water thin enough that the terahertz photons generated by the laser beam would not be absorbed, but thick enough to withstand the laser's energy.
Along with Yiwen E, a postdoctoral associate in Zhang's research group, Jin spent months optimizing the thickness of the water film and the incident angle, intensity, and pulse duration of the laser beam.
"We increased the thickness of the water a little bit, and gradually increased the laser, and just kept trying until we could make it work," Jin says. "Water is one of the richest resources on Earth, so it was really important for us to be able to generate these waves from water. There were many times I wanted to give up on this, but people in the lab kept encouraging me."
Zhang agrees: "I always tell my students and researchers here: if you try something, you might not get the result you wanted. But if you never try it, you definitely won't get it."


No comments:
Post a Comment