Oesophagus : Small hiatus hernia
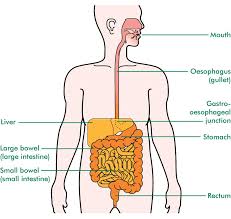
Oesophagus : The oesophagus is a long, muscular tube that connects your mouth to your stomach. It's around 25cm (10in) long in adults. When you swallow food, the walls of the oesophagus squeeze together (contract). This moves the food down the oesophagus to the stomach.
Small :
hiatus : hʌɪˈeɪtəs/ noun
a pause, break or interruption in the continuity of a work, series, action, etc. 2. a missing part; gap or lacuna
hernia : A hernia occurs when an organ pushes through an opening in the muscle or tissue that holds it in place. For example, the intestines may break through a weakened area in the abdominal wall. Hernias are most common in the abdomen, but they can also appear in the upper thigh, belly button, and groin areas.

Oesophagus : The oesophagus is a long, muscular tube that connects your mouth to your stomach. It's around 25cm (10in) long in adults. When you swallow food, the walls of the oesophagus squeeze together (contract). This moves the food down the oesophagus to the stomach.
Small :
smɔːl/
adjective
- 1.of a size that is less than normal or usual.
synonyms:
little, small-scale, compact, bijou; More - 2.insignificant; unimportant.
synonyms: slight, minor, unimportant, trifling, trivial, insignificant, inconsequential, inappreciable, inconsiderable, negligible, nugatory, paltry, infinitesimal;
hiatus : hʌɪˈeɪtəs/ noun
a pause, break or interruption in the continuity of a work, series, action, etc. 2. a missing part; gap or lacuna
hernia : A hernia occurs when an organ pushes through an opening in the muscle or tissue that holds it in place. For example, the intestines may break through a weakened area in the abdominal wall. Hernias are most common in the abdomen, but they can also appear in the upper thigh, belly button, and groin areas.

Any time an internal body part pushes into an area where it doesn't belong, it's called a hernia.
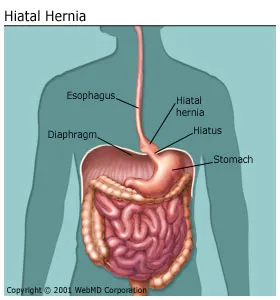
The hiatus is an opening in the diaphragm -- the muscular wall separating the chest cavity from the abdomen.
Normally, the esophagus (food pipe) goes through the hiatus and attaches to the stomach. In a hiatal hernia (also called hiatus hernia) the stomach bulges up into the chest through that opening.
There are two main types of hiatal hernias: sliding and paraesophageal (next to the esophagus).

In a sliding hiatal hernia, the stomach and the section of the esophagus that joins the stomach slide up into the chest through the hiatus. This is the more common type of hernia.
The paraesophageal hernia is less common, but is more cause for concern. The esophagus and stomach stay in their normal locations, but part of the stomach squeezes through the hiatus, landing it next to the esophagus. Although you can have this type of hernia without any symptoms, the danger is that the stomach can become "strangled," or have its blood supply shut off.
Many people with hiatal hernia have no symptoms, but others may have heartburn related to gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD. Although there appears to be a link, one condition does not seem to cause the other, because many people have a hiatal hernia without having GERD, and others have GERD without having a hiatal hernia.
People with heartburn may experience chest pain that can easily be confused with the pain of a heart attack. That's why it's so important to undergo testing and get properly diagnosed.


No comments:
Post a Comment